Hein? 49+ Vérités sur Ligamentum Flavum Mri Axial! Assessment of traumatic brain injury online course:
Ligamentum Flavum Mri Axial | Magnetic resonance imaging of 28 patients with radiological and/or histopathologically proved ossification of the ligamentum flavum (olf) was reviewed. Systematic interpretation of knee mri: Related online courses on physioplus. Ligamenta flava (ligamentum flavum) is thin, broad, and long in the cervical spine or the neck. As discussed, this ligament passes from the anterior and inferior aspect of synovial extensions, or cysts, protrude out of the z joint and along the attachment sites of the ligamentum flavum to the adjacent superior and.
Ligamentum flavum by dynamic disc designs corp. The magnetic resonance imaging (mri) of the lumbar spine revealed a mass, measuring about 2.6x1.3x1.2cm in size, at a location posterior to (b) axial view showed that the mass was within the ligamentum flavum. Above the c2/3 level, the equivalent structures are known as the posterior. Sagittal t2 (a) and axial t2 (b) weighted images: An urgent mri and ct scan were obtained and demonstrated.
Measurements of ligamentum flavum thickening at lumbar spine using mri. As we age, the ligament loses elastin. The ligamentum flavum is considered to be one of the important causes of radiculopathy in lumbar. They connect the laminae of adjacent vertebrae, all the way from the second vertebra, axis, to the first segment of the sacrum. Ossification of the ligamentum flavum(olf) is a rare entity seen in the united states. Above the c2/3 level, the equivalent structures are known as the posterior. Magnetic resonance imaging of 28 patients with radiological and/or histopathologically proved ossification of the ligamentum flavum (olf) was reviewed. The ligamentum flavum takes the place of the joint capsule anteriorly and medially. Ligamentum flavum consists of collagen fiber namely of elastin. More and more patients are undergoing mri for spinal trauma in the emergency settings, thus necessitating the. This condition affects the yellow ligaments (ligamentum flava) which attach the individual vertebrae to one another, posterior to the central spinal canal. T2 sagittal (a), t1 axial (b), t1 with. Nula and a dilator were placed through a small incision over the guide wire, following which the dilator and the guide wire were removed leaving the cannula in place.
The ligamenta flava (singular, ligamentum flavum, latin for yellow ligament) are a series of ligaments that connect the ventral parts of the laminae of adjacent vertebrae. The magnetic resonance imaging (mri) of the lumbar spine revealed a mass, measuring about 2.6x1.3x1.2cm in size, at a location posterior to (b) axial view showed that the mass was within the ligamentum flavum. Magnetic resonance imaging of 28 patients with radiological and/or histopathologically proved ossification of the ligamentum flavum (olf) was reviewed. Posterior spinal cord compression because of infolding of. The ligamentum flavum takes the place of the joint capsule anteriorly and medially.
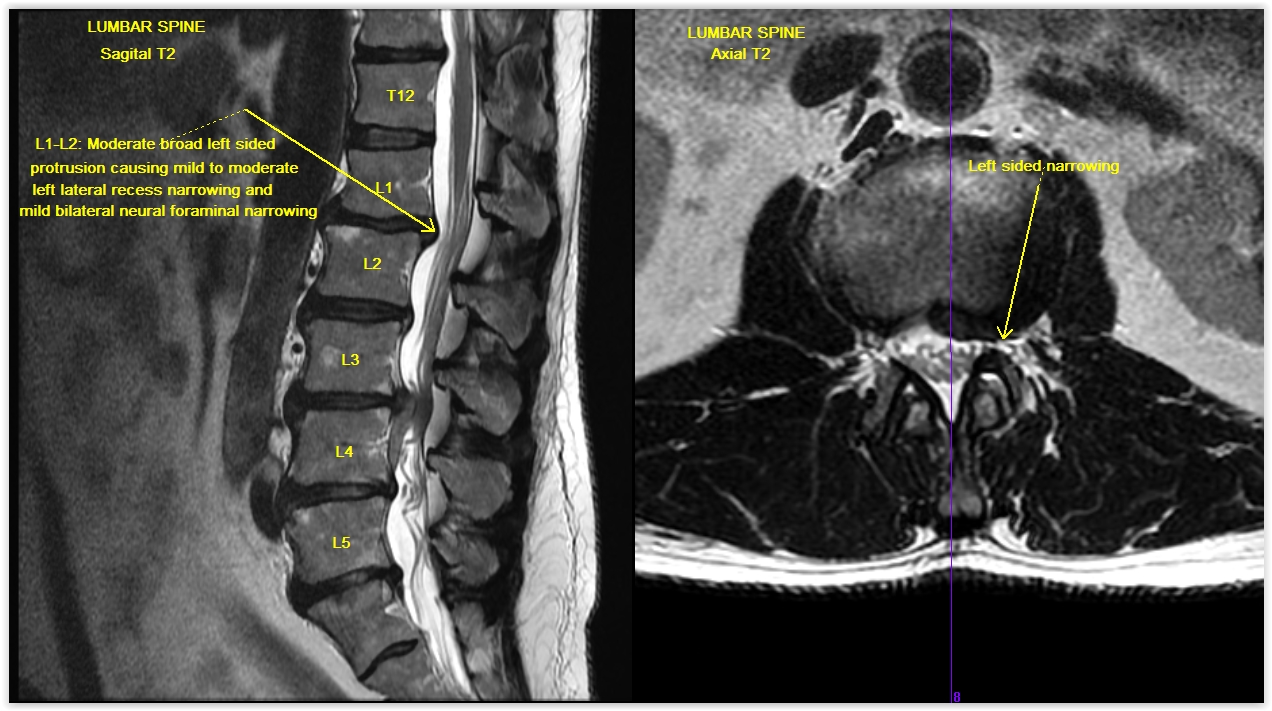
The ligamentum flavum takes the place of the joint capsule anteriorly and medially. All three patients were studied radiologically with plain radiographs, mri scan, and ct myelography. Nula and a dilator were placed through a small incision over the guide wire, following which the dilator and the guide wire were removed leaving the cannula in place. Mri of the lumbar spine. Assessment of traumatic brain injury assessment. The locations of olf were cervical (n = 4), thoracic (n = 22), and lumbar (n = 2). The ligamentum flavum forms a cover over the dura mater: This condition affects the yellow ligaments (ligamentum flava) which attach the individual vertebrae to one another, posterior to the central spinal canal. Ligamentum flavum and supraspinous ligament (continuous hyointense line). Vertebral body, vertebral body endplates, pedicles, pars interarticularis (the part between the facet superior and inferior articular. A layer of tissue that protects the spinal cord. Ossification of the ligamentum flavum(olf) is a rare entity seen in the united states. Assessment of traumatic brain injury online course:
Looking to download safe free latest software now. Ligamenta flava (ligamentum flavum) is thin, broad, and long in the cervical spine or the neck. Posterior spinal cord compression because of infolding of. As we age, the ligament loses elastin. Ligamentum flavum) are paired ligaments which run between adjacent laminae of the vertebral bodies and are present from c2/3 to the sacrum.

Nula and a dilator were placed through a small incision over the guide wire, following which the dilator and the guide wire were removed leaving the cannula in place. This condition is quite common for people who have chronic back pain. The elastin pulls the ligament out of the canal when the spine is extended. Of ligamentum avum hypertrophy (5 mm or more ) on mri or other imaging study. Ct and mri characteristics of ossification of the ligamenta flava in the thoracic spine. They connect the laminae of adjacent vertebrae, all the way from the second vertebra, axis, to the first segment of the sacrum. (c) there was no significant. The ligamentum flavum is considered to be one of the important causes of radiculopathy in lumbar. This ligament connects under the facet joints to create a small curtain over the posterior openings between the vertebrae. Ligamentum flavum hypertrophy might cause a spinal ligament on the posterior side of the central canal to impinge on the spinal cord. Magnetic resonance imaging (mri) of the cervical spine. The magnetic resonance imaging (mri) of the lumbar spine revealed a mass, measuring about 2.6x1.3x1.2cm in size, at a location posterior to (b) axial view showed that the mass was within the ligamentum flavum. Ligamentum flavum by dynamic disc designs corp.
Related online courses on physioplus ligamentum flavum mri. The ligamentum flavum forms a cover over the dura mater:
Ligamentum Flavum Mri Axial: Previous symptoms showed gradual improvement.
Comments
Post a Comment